Translated by Mahboube Khalvati
The following is a brief excerpt of Mohsen Ghanebasiri’s article entitled “Women and the Music Environment in Iran” published on the WomenofMusic.com on 21 January, 2013:
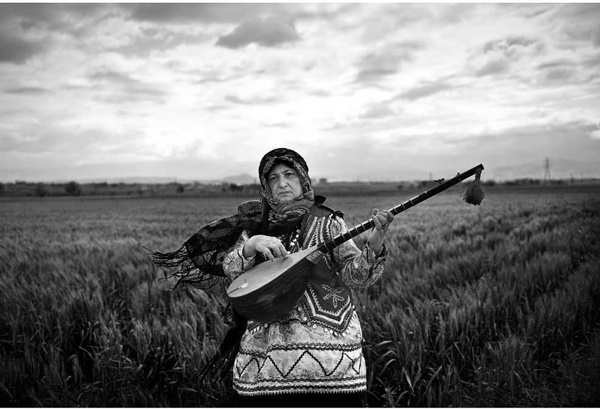
The life territory of the female-male relations in the Iranian cultural context is basically a domestic territory and not a social-living one in the labour and leisure domains. To prove this, it only suffices to consider the Iranian men’s viewpoints about women. For the Iranian men, there are three perspectives regarding the women: mother, sister and wife. Mother represents the emotional territory; sister represents the logical territory at home while wife represents the sexual territory.
All three characters are domestic ones and there is no indication of women as colleagues and companions sharing common goals. Consequently, the relations between the Iranian men with women are either limited to sexual issues or revolve around an emotional and highly oppressive look. Also, for women there are three kinds of men: father, brother and husband.
These relations differ from those mentioned above. The major issue for the women in these relations is obedience. Especially, in the framework of these relations, women’s engagement at work and leisure activities is considered as an offense. The only territory within which women can work is the household. Therefore, under these circumstances, women have no way but to have men come back home from the labour territory as quickly as possible.
For this reason, the very Iranian man has deprived himself from engagement in the leisure territory and from experiencing the spiritual relations which bring about solidarity; hence, the concept of creativity has turned into a challenge in our society. Moreover, the art which has been produced in our domestic environments in the course of our culture has been an abstract art with no traces of social issues. For instance, taking a look at the Iranian carpet patterns which resulted from the women’s labour at home one perceives this point. Their patterns are all abstract and isolated from the life realities.