Translated by Mahboube Khalvati
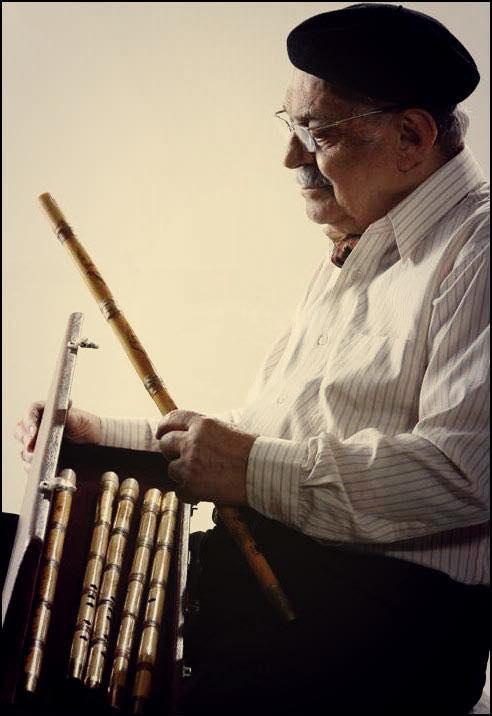
The name of Maestro Hassan Kassai is so vehemently intertwined with Ney (Persian reed flute) that one cannot imagine one without the other immediately coming into mind. Ney is one of the instruments which went through a lot of ups and downs in the history of the Iranian music since the time of Sassanid kings to the time when shepherds found playing it consoling when they took their cattle for grazing. However, Nay could never demonstrate its main capacities to gain a stable position among the musicians and the people like other instruments including Oud, Tar, Santour, all sorts of bowed string instruments and plucked string instruments.
Most probably, the simple procedure of making the instrument which had led to the emergence of nonstandard patterns and eventually the technical restrictions for Ney can be blamed for the lack of stability of Ney’s position in the Iranian music. In order to develop and increase the technical features of a musical instrument, it is necessary to primarily design its structure based on an exact and studied pattern and then make the instrument so that it becomes possible to play the instrument using its maximum capacity. Based on the available information on first Iranian music records, playing techniques for instruments such as Tar, violin and Kamancheh are more sophisticated. The only available old recording of Ney is of solo playing and avaaz accompaniment by Nayeb Asadollah Esfahani who is believed to be the first musician playing Ney by the means of “teeth”. In any case, by examining the available old records, one can learn about the level of playing Ney in the past.
Maestro Kassai could not benefit from the teachings of Nayeb directly but received lessons from one of Nayeb’s pupils, Mehdi Navai; this fact proves, on the one hand, Kassai’s depth of talent and, on the other hand, the limitations and simplicity of Ney’s techniques. In this sense, Hassan Kassai is like Tehrani in Tonbak, Ahmad Ebadi in Setar, Asghar Bahari in Kamancheh and Faramarz Payvar in Santour, in devising techniques and playing all dastgahs by Ney.
In the past, the sound of Ney was impure, in other words, Ney was played in a way that one could not distinguish between different pitches; however, through changes in the position of the tongue, lips and the shape of the mouthpiece, Maestro Kassai could produce a clear and pure sound out of the instrument. This progress made the Maestro’s Ney find its way to the state radio. Consequently, solo performances and accompanying famous instrumentalists and singers such as Jalil Shahnaz, Ali Tajvidi, Ahmad Ebadi, Taj Esfahani, Adib Khansari, etc. promoted Ney to the same level as other Iranian instruments.
After this period, most of Iranian orchestras started using Ney and this need led to the ever-increasing number of Ney players with Ney becoming a field taught at universities as a specialized course. We can say that, today’s Ney players became interested in the instrument after listening to Maestro Kassai Ney.
According to Hassan Kassai, he was born on 26 September 1926 in a family of businessmen. His father, Seyed Javad Kassai, was one of the famous businessmen in Esfahan. Seyed Javad Kassai loved music and his house was a place for gatherings of famous Esfahani maestros such as Seyed Hossein Taherzadeh, Jalal Tajzadeh Esfahani, Akbar Khan Nowrouzi, the Shahnaz family (Shaban Khan, Hossen Agha, Ali Agha and Jalil Shahnaz), Gholam Hossein Saranj and Adib Khansari.
These reunions familiarized Hassan Kassai with the Iranian music from an early age and his passion for music especially Ney (after he saw an itinerant Ney player) made his father take him to Ney lessons by Mehdi Navai. After Mehdi Navai’s death, Kassai took advantage of interactions and collaborations with Esfahani musiscians to further master playing Ney. He especially learned a lot from Jalil Shahnaz to whom he is indebted. Playing Ney accompanied by fretted instruments such as Tar and Setar made Kassai more familiar with different scales of the Iranian music to the extent that he played Chahargah, Esfahan, Nava and Rastpanjgah with an exact tuning and completely for the first time. Kassai is also indebted to Abolhassan Saba and his knowledge of Setar is a legacy of the time he spent with the unique senior musician. Kassai’s style of playing Setar is a combination of Jalil Shahnaz’s Tar-playing style and Abolhassan Saba’s Setar style.
For years, Hassan Kassai taught Ney, Setar and Avaz. Many pupils attended his classes in person and many famous musicians benefited from his lessons on the radio including Hossein Omoumi, Hassan Nahid, Mohammad Mousavi, Behzad Forouhari, Nematollah Sotoudeh and Shahram Mirjalali. Although many of Kassai’s pieces were improvisation rather than composed music, today a lot of pieces and Avaz played by Ney players owe to his performances.