The Nose Technique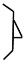
When the author was working on the piece “Playing Love” by Ennio Morricone (from the legend of 1900), he realized a failure of the Lip Technique. Needing to play a chord in the 14th position of the guitar and in order to complete the harmony, it is necessary to play a harmonic note on the 7th or 5th position; it was not possible to touch the string to play this harmonic note, because the Lip Technique is used for getting the notes and not to touch the string and producing harmonic notes. Naturally, the only possible way to touch the string was to use the nose at the required position and playing the note with the right hand, and this was the best option the author found to how to play such harmonic notes, and where Needing to play a chord “on” the 14th position was generated.
The technique represented here should not be mistaken with a previously published personal video of a group of guitar masters, where David Russell with a few others of his friends played different effects on the guitar; which in a part of that video, plays a harmonic note with nose for fun. Also another place the author has seen something similar to this technique is the book “Questions and Answers about the Classic Guitar”, where the author of this book Sharon Isbin, mentions a play of a famous classical guitar player, as follows: “in recording one piece, in order to stop the sound of the 6th string, the nose was used …” (which stopping the sound of the string is something different from playing a harmonic note).
All the aforementioned was to remind that the “Nose Technique” is a complementary technique for the “Lip Technique” and not by any means an act of jocosity. The author has developed these two complementary techniques as a procedure to play a complete melody line independent of the fingers of the left hand, and not only for playing a single note on a string while playing a piece (however, the author has not found any method in world, similar to the “Lip Technique” introduced in this manuscript).
“Consider a musician of classical guitar, playing a part of a harmony in a piece with the left hand and simultaneously the lip and nose are situated at different positions and even opposite to the movement of the left hand, playing another part of the harmony and the melody line in the piece. This technique introduces a new method in classical guitar and even other styles of guitar.”
With no doubt, as same as the “Lip Technique”, exercise is also necessary for the “Nose Technique” as well. Exercises such as playing harmonics on a string, along the length of the fingerboard, and playing wide-apart harmonics, such as: the 3rd and 12th positions on the three bass strings could improve capabilities of the musician.
Significant points about applying the Nose Technique:
1- Taking care about making sudden moves with the neck, as same as the Lip Technique.
2- Being careful when the face gets very close to the fingerboard of the guitar, the eye sight may become limited or blocked, therefore control on the fingers of the left hand would be a priority; because in opposite movements of the left hand in compare to the lip and nose, it would not be possible to observe and control the fingering on the left hand fingers.
3- Finally, a point when using this technique is the possibility of an itching since of the nose. For restricting such an event, it is suggested to clean the strings with a little moistened cloth, besides not having an oily skin surface of the nose while applying this technique.
Advantages and Restrictions of the “Lip” and “Nose” techniques
1- The significant advantage of these techniques is making it possible to play harmonies and intervals which till now had to be eliminated or replaced with other notes, in order to be playable with the classical guitar, because of their wide-apart intervals, which could be only for playing a single note or creating a complete melody-line independent of the left hand fingers.
2- The first restriction of these techniques is anatomic differences in the size and form of the lip and nose of each person, which influence of this parameter on applying these techniques needs independent research, based on experience of different musicians applying these techniques (possibly to be the subject of a separate manuscript).
3- Another restriction is not being able to apply the Lip Technique beyond the 12th position; because the fingerboard is situated on the sound board or top of the guitar and therefore it would not be possible to get notes with the Lip for such positions. This failure was understood by the author while arranging “Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, BWV 582” by Johann Sebastian Bach, on the classical guitar, while trying to preserve the original tonality. Which in order to overcome this restriction a subsidiary technique, named by the author as the “Chin Technique” is developed.
The Chin Technique is applied for situations such as needing to play a note with the Lip on the 6th string and 14th position of the guitar, which the only possible way the author could apply, was using the graphic sign ( )or the “Chin Technique” for playing this note. Although the “Chin Technique” could be considered a technique independent from the Lip technique, the author has considered it a subsidiary of the Lip technique. In the Chin Technique the required note is taken applying the left corner of the chin and the stroke of the right hand fingers (picture No.3). The author suggests this technique for positions beyond the 12th position, because except such positions it is much more practical to apply the Lip Technique.
)or the “Chin Technique” for playing this note. Although the “Chin Technique” could be considered a technique independent from the Lip technique, the author has considered it a subsidiary of the Lip technique. In the Chin Technique the required note is taken applying the left corner of the chin and the stroke of the right hand fingers (picture No.3). The author suggests this technique for positions beyond the 12th position, because except such positions it is much more practical to apply the Lip Technique.

(picture No.3)
4- The last restriction is when needed to play a chord on the 2nd position and simultaneously a note on the 14th position of the 1st string. In such situation none of the aforementioned techniques could be applied, unless playing a sound similar to the harmonic of that note on another string. If that would not be possible either, then like playing an electric guitar, with the “i” finger (of the right hand) we get the note on the 1st string and with fingers “a” or “x” could play that note (picture No.4).
As the closure of this manuscript, in the following video, the author has played an arrangement of  “Playing Love” aforementioned within the text, in order to illustrate application of the aforementioned techniques (Lip and Nose Techniques), and capabilities they give the classical guitar to preserve the original tonality of the piece.
“Playing Love” aforementioned within the text, in order to illustrate application of the aforementioned techniques (Lip and Nose Techniques), and capabilities they give the classical guitar to preserve the original tonality of the piece.

(picture No.4)
I hereby appreciate all friends of mine and masters who assisted my work. I present my gratitude to my dear cousin Dr. Farzad Mahdavi, who is such as a brother to me, for his valuable guidance and assistance in all stages of preparing this manuscript. I respect my dear professor Dr. Loris Hovian for all his kind support in reviewing the pieces and finally Mr. Sajad Pourghanad the director the Harmony-Talk website.
New Technique for Playing Classical Guitar in youtube
References
1- Bosman, L. 1998. Harmony for Guitar (Guitar Magazine Project). Music Sales America. New York.
2- Sharon, I. 1999. Classical Guitar Answer Book. Hal Leonard Corporation. Milwaukee, USA.
3. Dyens, Roland. 1994. Libra Sonatine. Henry Lemoine. Paris.
4. Villa-Lobos, Heitor. 1992. Dyens, Roland (Adaptation pour Guitar Solo). Aria de La Bachianas Brasileiras No.5. Henry Lemoine. Paris.
5. Ramirez, Ariel. © 2006. Dyens, Roland (Arranged for guitar solo). Alfonsina y el mar (1921). Les Productions d’OZ (DZ.DZ-980). Québec.
6. Mussorgsky, Modest Petrovich. 1981. Yamashita, Kazuhito (Arranged for Guitar). Pictures at an Exhibition, (1874). Gendai Guitar Magazine. Tokyo.
7. Dvorak, Antonin. 1986. Yamashita, Kazuhito(Arranged for Guitar). From the New world (Symphony No.9 in E-Minor Op.95). Gendai Guitar Magazine. Tokyo.
8. Moussorgsky, Modest. © 1950. Bauer, Harlod (Transcribed for the piano). Pictures at an Exhibition. G. Schirmer. New York.
9. thewholeguitarist.com [May 28, 2015]
10. guitarandluteissues.com [May 28, 2015]
11. Lee, Chen-Tien. 1993. Mussorgsky’s Pictures at an Exhibition: An analytical and performance study (D.M.A. Document). The Ohio State University.
12. en.wikipedia.org [May 28, 2015]
13. pianostreet.com [May 28, 2015]
14. imslp.org [May 28, 2015]
15. Morricone, Ennio. 1999. Playing Love (The Legend of 1900, original motion picture soundtrack). Sony Classical.
16. sheetmusicdownload.in [May 28, 2015]
17. morricone.cn [May 28, 2015]
18. lipaugmentation.com [May 28, 2015]
19. en.wikipedia.org [May 28, 2015]
20. spine-health.com [May 28, 2015]









