Introduction
The world of music has unparalleled respect for Bach. Bach is considered the spiritual father of classical music; Bach’s great position is due not only to his great achievements in the fields of harmony, counterpoint, and compositional sciences but also to his respect for and adherence to the artistic principles of classical music. In the history of classical music, it is recorded that Bach walked about fifty kilometers to listen to the music played by the great German organist Dieterich Buxtehude, and this is the path that every idealistic classical music student should walk.
“Road to Bach” is just as instructive and admirable in terms of considering theoretical issues of music. Unlike many composers of the early twentieth century, whose “corrupt successors” unwantedly caused a crisis in classical music, Bach had influential successors in theoretical matters.
We know that in Bach’s time there was no harmonic analysis as there is today, and Bach’s main reference for the direction of the chords was only his unique hearing sense.
Recently, the prominent Japanese pianist, Kotaro Fukuma, commissioned a young Iranian composer Farhad Poupel, to write a piece with the theme of Bach. In this project called “Road to Bach”, the young Iranian composer has created a piece called “Road to Bach” which is reminiscent of Bach’s method in composing. In fact, drawing on Bach’s approach to harmony (i.e., paying attention to the aesthetics of sounds and not just studying the works of the past), Poupel has tried to find a way to compose on the basis of harmonic motion. Although this harmonic progression does not completely follow the traditional harmonic progression, it has clearly a strong harmonic movement.
The score of the piece is published by Musepress in Japan
Characteristics of “Road to Bach”
1- Extensive Chromatism: At the beginning of this piece, a monophonic theme is first introduced in the Persian mode, “Charghaah”, and the theme is then expanded; however, the composer avoids being in the mode completely by using extensive chromaticism
2- A piano in the role of two pianos: There are parts in this piece where the musician has to make two separate sonorities from the piano*. The most important challenge is that these parts are placed between the pianists’ hands and the pianist cannot easily prepare one hand to perform a specific sonority, and it is necessary to carefully maintain the priority of the turbulent melodic line between difficult chords and passages.
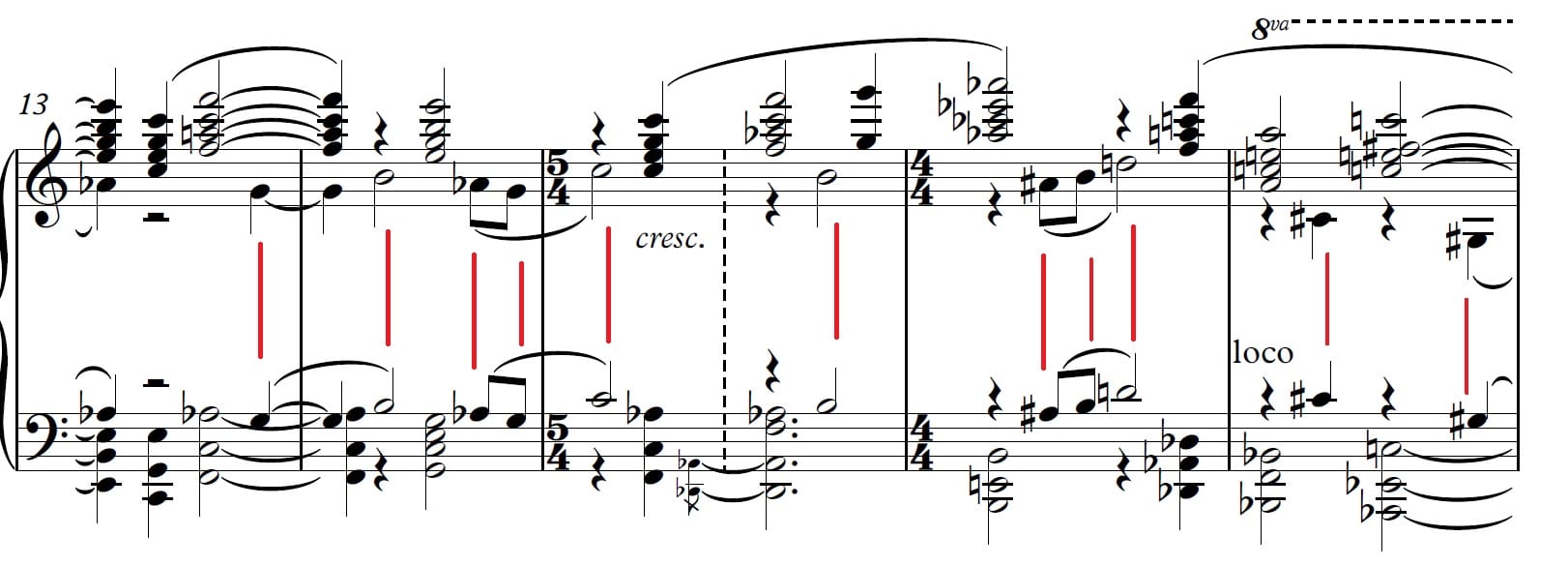
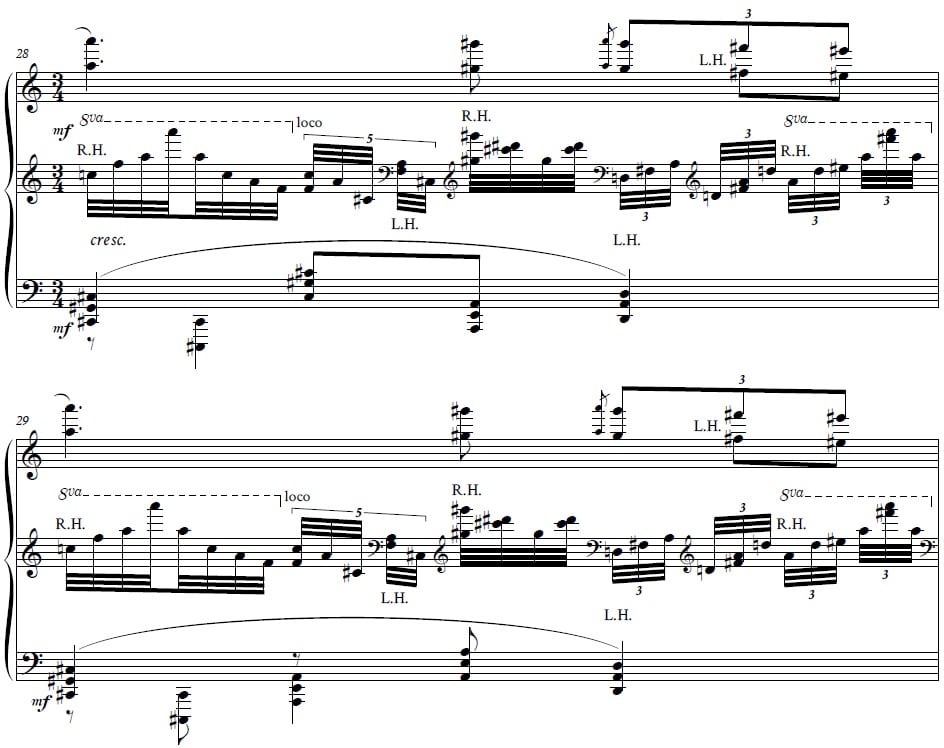


3- Different but progressive harmony: Perhaps three general parts can be identified in this work: the first part (from the beginning of the piece to bar no. 39) can be described as the “dark part”, the second part (from bar no. 40 to 70) “The light part” and the third part (from the bar no. of 71 to the end of the piece) “Gray part “. In the first part, which is inspired by the Persian mode, Chahrgaah, special and unfamiliar chords are seen compared to the tonal triads, and naturally, the connection of the chords is more vague and weak. In the second part, in which the “major” mode is dominant, the chords are closer to the traditional, tonal harmony and the connection of the chords is clearer. In the third part, the conflict between the two themes of “major” and “Chahargah ” causes original harmonic movement that eventually ends in Major chords and a bright atmosphere. Perhaps the Coda of this work can be considered the most brilliant part of this music in terms of harmony, because the composer, in a creative combination, tries to dissolve the dissonant chords outside the normal tonal harmonies in the consonant, triadic chords.
4- Piano techniques: Farhad Poupel, who plays the piano himself, has paid special attention to piano techniques and their possibilities; despite all the technical difficulties, this piece is completely pianistic and applicable for professionals and virtuoso pianists. All the guides on the score provide the path to play the piece as the composer wants. For example, at the end of the piece, the composer wants the two sets of simple chords and lunato (meaning “far away”) to be performed as if they were two separate sounds. Also, in the sections that are mentioned separately for the pianist, all the situations are well coordinated with the possibilities of this instrument.

5- Form: This work begins with the introduction of a theme in the “Chahargah” mode and from bar no. 20, the development of this theme starts and continues until the second part, which is the beginning of the Major section in the bar no. 40. In this section, comes a theme that Bach has used. In the third part, we hear the transformation of the second theme in the first theme with the alteration of the first theme, which indicates the Coda of this work.
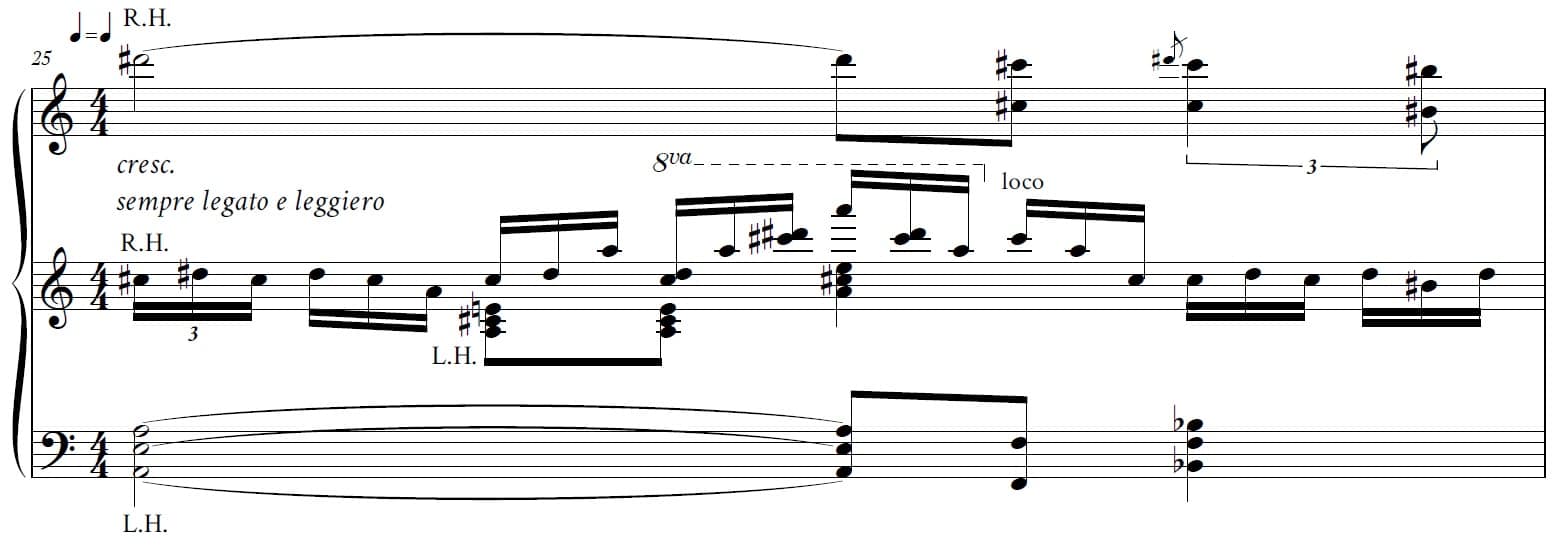

* Since Farhad Popel wrote this piece for Kotaro Fukuma, a prominent Japanese pianist, and was aware of his ability to perform a variety of colorings on this piece, these colorings were specifically written for the piano.
Art of Music Magazine