Translated by Mahboube Khalvati

Soudeh Mofidi (An RZW member since 2012)
In this project, my specialized responsibility was the basic drawings of the desired instrument with the help of engineering and mechanical software. I have also the carried out phases related to engineering designs, related variables, and volume and weight calculations under Mr. Ziaei’s direct supervision from the very beginning. Regarding the challenges of this work, suffice it to say that the set of designs for the instrument lasted more than 9 months in the final stage of the project only.

Farzad Shalpoush (An RZW member since 2015)
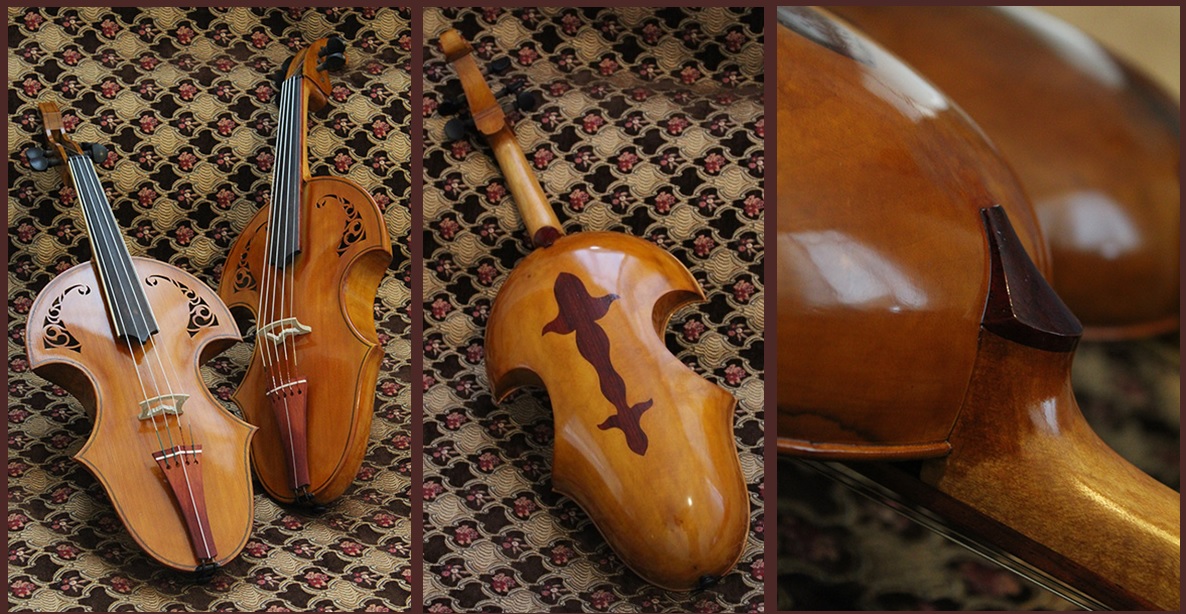
My contribution to this project includes designing some visual elements, for example, sound holes and designs of decorative elements based on the Iranian aesthetics, doing the stages for making and assembling necks, preparing and varnishing, assisting in reaching the desired thickness for plates and assisting in technical designing and making pieces such as tail pieces. Due to the difficulties and subtleties of neck structures, decorative elements and sound holes, the project faced considerable technical complications; however, we tried to do it with an optimal quality.

Neda Asadinejad (An RZW member since 2014)
My responsibilities in this project included assisting with designing sound holes, designing and preparing early samples of the neck structure according to the Iranian aesthetics, making parts such as saddle and nuts and participating in research phases.
Considering that in redesigning the parts of a structure such as an instrument both aesthetic elements and mechanical, acoustic and physical principles should be taken into account, finding an optimal balance point for redesigning visual elements of the instrument was as one of the challenges of the project.
Farshad Shalpoush (An RZW member since 2016)
Assisting with carving and preparing patterns, determining the thickness of the bowl, making fingerboards and making neck heel button consisted the majority of my responsibilities in this project. I also collaborated in the early stages of preparing executive patterns, preparing colors and color coating and some other executive activities. Compared to the previous samples, the thickness of the bowls in the new samples has been considered with special sensitivity to stabilize the acoustic properties, to the extent that the variation of the thickness in different areas has been achieved through a new perspective. This important point carries a set of subtleties and difficulties for implementation.
Amir Khamseh (An RZW member since 2012)
My job description in this project encompassed participation in designing some instrument components including early samples of sound holes and neck structure based on the Iranian aesthetics, preparing early samples of plates, contribution to designing and making an exclusive bridge for the new instrument based on acoustic demands, preparation of three-dimensional models of the instrument using engineering software, historical research and research related to the Iranian aesthetics and physics of the instrument, i.e., calculations of the volume of the resonating air and the area of sound holes. When it comes to a project of this magnitude, it is necessary to be ready at any moment for a change or for taking a measure for improving the instrument, especially considering the complexity of the activity as a whole and various opinions. Such challenges can only be overcome through empathy.
Final Words
It should be noted that in addition to the main and permanent members of the current RZW team who have been permanently involved in the new project, other individuals, including Mr. Khoshbakhti, one of the old workshop members, have participated in the process of making the improved pattern. We would like to use this opportunity and appreciate him. Also, we would like to express our thanks to other friends who have cooperated with us at some stages of this project for a limited period of time: Mr. Saeed Jalali, for making the initial version of the molds of bowls of ribs; Ms. Sara Issazadeh and Ms. Nadia Shalpoush, for doing some phases of gouging bowls, plates and sound holes for early versions of the instrument.